Page 43 - 2023-bfw-physics-stewart-3e-new.indd
P. 43
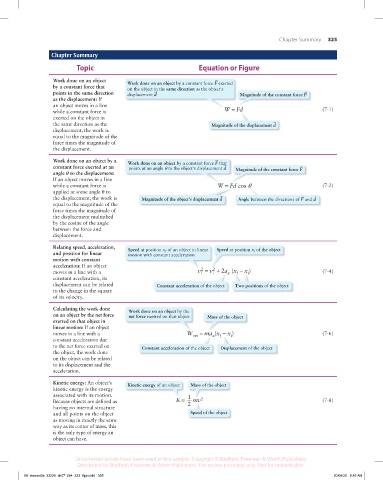
Chapter Summary 325
Chapter Summary
Topic Equation or Figure
Work done on an object Work done on an object by a constant force F exerted
by a constant force that on the object in the same direction as the object's
points in the same direction displacement d Magnitude of the constant force F
as the displacement: If
an object moves in a line
while a constant force is W = Fd (7-1)
exerted on the object in
the same direction as the Magnitude of the displacement d
displacement, the work is
equal to the magnitude of the
force times the magnitude of
the displacement.
Work done on an object by a Work done on an object by a constant force F that
constant force exerted at an points at an angle q to the object’s displacement d Magnitude of the constant force F
angle θθ to the displacement:
If an object moves in a line
while a constant force is W = Fd cos q (7-2)
applied at some angle θ to
the displacement, the work is Magnitude of the object’s displacement d Angle between the directions of F and d
equal to the magnitude of the
force times the magnitude of
the displacement multiplied
by the cosine of the angle
between the force and
displacement.
Relating speed, acceleration,
i
f
and position for linear Speed at position x of an object in linear Speed at position x of the object
motion with constant acceleration
motion with constant
acceleration: If an object
2
2
moves in a line with a v = v + 2a (x − x ) (7-4)
f
i
f
i
x
constant acceleration, its
displacement can be related Constant acceleration of the object Two positions of the object
to the change in the square
of its velocity.
Calculating the work done
on an object by the net force Work done on an object by the Mass of the object
net force exerted on that object
exerted on that object in
linear motion: If an object
moves in a line with a W = ma (x − x ) (7-6)
net
f
i
x
constant acceleration due
to the net force exerted on Constant acceleration of the object Displacement of the object
the object, the work done
on the object can be related
to its displacement and the
acceleration.
Kinetic energy: An object’s Kinetic energy of an object Mass of the object
kinetic energy is the energy
associated with its motion. 1
Because objects are defined as K = 2 mv 2 (7-8)
having no internal structure
and all points on the object Speed of the object
as moving in exactly the same
way as its center of mass, this
is the only type of energy an
object can have.
Uncorrected proofs have been used in this sample. Copyright © Bedford, Freeman & Worth Publishers.
Distributed by Bedford, Freeman & Worth Publishers. For review purposes only. Not for redistribution.
08_stewart3e_33228_ch07_284_333_8pp.indd 325 20/08/22 8:46 AM