Page 48 - 2024-bfw-MyersAP4e
P. 48
®
AP Science Practice Check Your Understanding
Examine the Concept Apply the Concept
▶ ▶Explain how a stimulant affects behavior. ▶ ▶Think of a friend or family member who is addicted to
▶ ▶Explain the physiological effects of nicotine. nicotine. What do you think would be most effective to say to
▶ ▶Explain the withdrawal symptoms someone should expect that person to convince them to try to quit?
when quitting smoking.
Answers to the Examine the Concept questions can be found in Appendix C at the end of the book.
molecule Distributed by Bedford, Freeman & Worth Publishers. Not for redistribution.
Cocaine
®
AP Exam Tip
Cocaine is a powerfully addictive stimulant derived from the coca plant. The recipe for
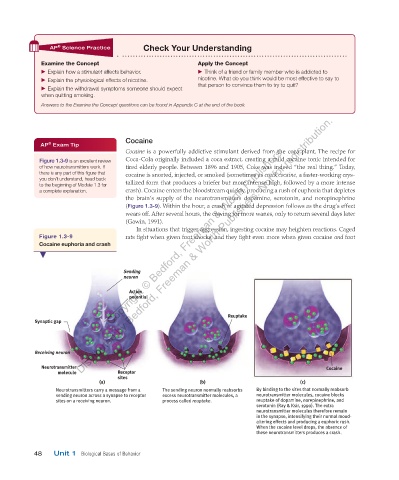
Figure 1.3-9 is an excellent review Coca-Cola originally included a coca extract, creating a mild cocaine tonic intended for
of how neurotransmitters work. If tired elderly people. Between 1896 and 1905, Coke was indeed “the real thing.” Today,
there is any part of this figure that cocaine is snorted, injected, or smoked (sometimes as crack cocaine, a faster-working crys-
you don’t understand, head back tallized form that produces a briefer but more intense high, followed by a more intense
to the beginning of Module 1.3 for
a complete explanation. crash). Cocaine enters the bloodstream quickly, producing a rush of euphoria that depletes
the brain’s supply of the neurotransmitters dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine
(Figure 1.3-9). Within the hour, a crash of agitated depression follows as the drug’s effect
wears off. After several hours, the craving for more wanes, only to return several days later
(Gawin, 1991).
In situations that trigger aggression, ingesting cocaine may heighten reactions. Caged
Figure 1.3-9 Copyright © Bedford, Freeman & Worth Publishers.
rats fight when given foot shocks, and they fight even more when given cocaine and foot
Cocaine euphoria and crash
Sending
neuron
Action
potential
Reuptake
Synaptic gap
Receiving neuron
Neurotransmitter Cocaine
Receptor
sites
(a) (b) (c)
Neurotransmitters carry a message from a The sending neuron normally reabsorbs By binding to the sites that normally reabsorb
sending neuron across a synapse to receptor excess neurotransmitter molecules, a neurotransmitter molecules, cocaine blocks
sites on a receiving neuron. process called reuptake. reuptake of dopamine, norepinephrine, and
serotonin (Ray & Ksir, 1990). The extra
neurotransmitter molecules therefore remain
in the synapse, intensifying their normal mood-
altering effects and producing a euphoric rush.
When the cocaine level drops, the absence of
these neurotransmitters produces a crash.
48 Unit 1 Biological Bases of Behavior
03_myersAPpsychology4e_28116_ch01_002_163.indd 48 15/12/23 9:22 AM