Page 5 - 2023-ml-myers-pel6e-chapter7-sample
P. 5
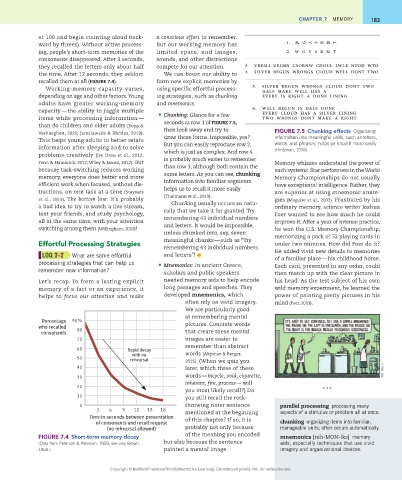
at 100 and begin counting aloud back- a conscious effort to remember. CHAPtER 7 MeMory 183
ward by threes). Without active process- But our working memory has 1. W G V S R M T
ing, people’s short- term memories of the limited space, and images, 2. W G V S R M T
consonants disappeared. After 3 seconds, sounds, and other distractions
they recalled the letters only about half compete for our attention. 3. VRESLI UEGBN GSORNW CDOUL LWLE NTOD WTO
the time. After 12 seconds, they seldom We can boost our ability to 4. SILVER BEGUN WRONGS CLOUD WELL DONT TWO
recalled them at all (FIGURE 7.4). form new explicit memories by
Working- memory capacity varies, using specific effortful process- 5. SILVER BEGUN WRONGS CLOUD DONT TWO
HALF MAKE WELL HAS A
depending on age and other factors. Young ing strategies, such as chunking EVERY IS RIGHT A DONE LINING
adults have greater working- memory and mnemonics.
capacity — the ability to juggle multiple 6. WELL BEGUN IS HALF DONE
EVERY CLOUD HAS A SILVER LINING
items while processing information — • Chunking: Glance for a few TWO WRONGS DONT MAKE A RIGHT
than do children and older adults (Bopp & seconds at row 1 of FIGURE 7.5,
Verhaeghen, 2020; Jaroslawska & Rhodes, 2019). then look away and try to FIGURE 7.5 Chunking effects Organizing
This helps young adults to better retain draw those forms. Impossible, yes? information into meaningful units, such as letters,
words, and phrases, helps us recall it more easily
information after sleeping and to solve But you can easily reproduce row 2, (Hintzman, 1978).
problems creatively (De Dreu et al., 2012; which is just as complex. And row 4
Fenn & Hambrick, 2012; Wiley & Jarosz, 2012). But is probably much easier to remember Memory whizzes understand the power of
because task- switching reduces working than row 3, although both contain the such systems. Star performers in the World
memory, everyone does better and more same letters. As you can see, chunking Memory Championships do not usually
efficient work when focused, without dis- information into familiar segments have exceptional intelligence. Rather, they
tractions, on one task at a time (Steyvers helps us to recall it more easily are superior at using mnemonic strate-
et al., 2019). The bottom line: It’s probably (Thalmann et al., 2019). gies (Maguire et al., 2003). Frustrated by his
a bad idea to try to watch a live stream, Chunking usually occurs so natu- ordinary memory, science writer Joshua
text your friends, and study psychology, rally that we take it for granted. Try Foer wanted to see how much he could
all at the same time, with your attention remembering 43 individual numbers improve it. After a year of intense practice,
switching among them (Willingham, 2010)! and letters. It would be impossible, he won the U.S. Memory Championship,
unless chunked into, say, seven memorizing a pack of 52 playing cards in
Effortful Processing Strategies meaningful chunks — such as “Try under two minutes. How did Foer do it?
remembering 43 individual numbers
LOQ 7-7 What are some effortful and letters”! He added vivid new details to memories
processing strategies that can help us • Mnemonics: In ancient Greece, of a familiar place — his childhood home.
Each card, presented in any order, could
remember new information? scholars and public speakers then match up with the clear picture in
Let’s recap. To form a lasting explicit needed memory aids to help encode his head. As the test subject of his own
memory of a fact or an experience, it long passages and speeches. They wild memory experiment, he learned the
helps to focus our attention and make developed mnemonics, which power of painting pretty pictures in his
often rely on vivid imagery. mind (Foer, 2011).
We are particularly good
at remembering mental
Percentage 90%
who recalled 80 pictures. Concrete words
consonants that create these mental
70 images are easier to
remember than abstract
60 Rapid decay
with no words (Akpinar & Berger,
50 rehearsal 2015). (When we quiz you
40 later, which three of these Tom Gauld
30 words — bicycle, void, cigarette,
inherent, fire, process — will
20
you most likely recall?) Do * * *
10 you still recall the rock-
0 throwing rioter sentence parallel processing processing many
3 6 9 12 15 18 mentioned at the beginning aspects of a stimulus or problem all at once.
Time in seconds between presentation of this chapter? If so, it is
of consonants and recall request chunking organizing items into familiar,
(no rehearsal allowed) probably not only because manageable units; often occurs automatically.
FIGURE 7.4 Short- term memory decay of the meaning you encoded mnemonics [nih- MON- iks] memory
(Data from Peterson & Peterson, 1959; see also Brown, but also because the sentence aids, especially techniques that use vivid
1958.) painted a mental image. imagery and organizational devices.
Copyright © Bedford/Freeman/Worth/Macmillan Learning. Uncorrected proofs. Not for redistribution.
08_pel6e_41872_ch07_179_201.indd 183 11/03/22 4:33 PM