Page 49 - 2022-bfw-morris-1e
P. 49
a tetrahedron, and the four covalent bonds with H extend
the H atoms toward the four corners of this structure.
Because of its shape and because its single bonds rotate
©2022 BFW Publishers. PAGES NOT FINAL. For review purposes only - do not post.
freely, carbon is able to make compounds in a variety of
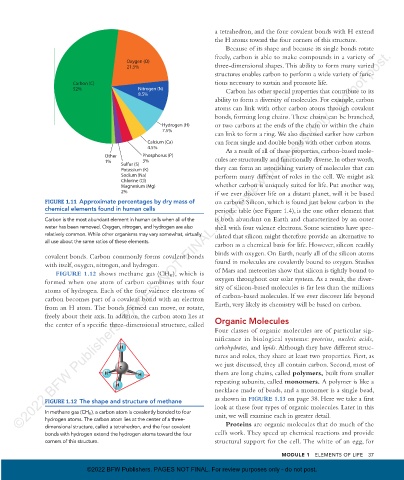
Oxygen (O)
21.5% three- dimensional shapes. This ability to form many varied
structures enables carbon to perform a wide variety of func-
Carbon (C) tions necessary to sustain and promote life.
52% Nitrogen (N) Carbon has other special properties that contribute to its
8.5%
ability to form a diversity of molecules. For example, carbon
atoms can link with other carbon atoms through covalent
bonds, forming long chains. These chains can be branched,
Hydrogen (H) or two carbons at the ends of the chain or within the chain
7.5%
can link to form a ring. We also discussed earlier how carbon
Calcium (Ca) can form single and double bonds with other carbon atoms.
4.5% As a result of all of these properties, carbon- based mole-
Other Phosphorus (P)
1% 3% cules are structurally and functionally diverse. In other words,
Sulfur (S)
Potassium (K) they can form an astonishing variety of molecules that can
Sodium (Na) perform many different of roles in the cell. We might ask
Chlorine (Cl)
Magnesium (Mg) whether carbon is uniquely suited for life. Put another way,
2% if we ever discover life on a distant planet, will it be based
FIGURE 1.11 Approximate percentages by dry mass of on carbon? Silicon, which is found just below carbon in the
chemical elements found in human cells periodic table (see Figure 1.4), is the one other element that
Carbon is the most abundant element in human cells when all of the is both abundant on Earth and characterized by an outer
water has been removed. Oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen are also shell with four valence electrons. Some scientists have spec-
relatively common. While other organisms may vary somewhat, virtually ulated that silicon might therefore provide an alternative to
all use about the same ratios of these elements.
carbon as a chemical basis for life. However, silicon readily
binds with oxygen. On Earth, nearly all of the silicon atoms
covalent bonds. Carbon commonly forms covalent bonds
with itself, oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen. found in molecules are covalently bound to oxygen. Studies
FIGURE 1.12 shows methane gas (CH), which is of Mars and meteorites show that silicon is tightly bound to
4
formed when one atom of carbon combines with four oxygen throughout our solar system. As a result, the diver-
atoms of hydrogen. Each of the four valence electrons of sity of silicon- based molecules is far less than the millions
carbon becomes part of a covalent bond with an electron of carbon- based molecules. If we ever discover life beyond
from an H atom. The bonds formed can move, or rotate, Earth, very likely its chemistry will be based on carbon.
freely about their axis. In addition, the carbon atom lies at Organic Molecules
the center of a specific three- dimensional structure, called
Four classes of organic molecules are of particular sig-
nificance in biological systems: proteins, nucleic acids,
H carbohydrates, and lipids. Although they have different struc-
tures and roles, they share at least two properties. First, as
we just discussed, they all contain carbon. Second, most of
C
H H them are long chains, called polymers, built from smaller
repeating subunits, called monomers. A polymer is like a
H
necklace made of beads, and a monomer is a single bead,
FIGURE 1.12 The shape and structure of methane as shown in FIGURE 1.13 on page 38. Here we take a first
look at these four types of organic molecules. Later in this
In methane gas (CH), a carbon atom is covalently bonded to four unit, we will examine each in greater detail.
4
hydrogen atoms. The carbon atom lies at the center of a three-
dimensional structure, called a tetrahedron, and the four covalent Proteins are organic molecules that do much of the
bonds with hydrogen extend the hydrogen atoms toward the four cell’s work. They speed up chemical reactions and provide
corners of this structure. structural support for the cell. The white of an egg, for
MODULE 1 ELEMENTS OF LIFE 37
©2022 BFW Publishers. PAGES NOT FINAL. For review purposes only - do not post.
04_morrisapbiology1e_11331_Unit1_Mod1_26-42_3pp.indd 37 10/04/21 9:10 AM