Page 46 - Demo
P. 46
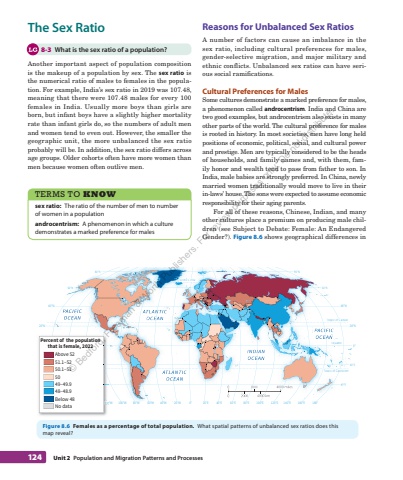
124 Unit 2 Population and Migration%u00a0Patterns and%u00a0Processes Reasons for Unbalanced Sex Ratios A number of factors can cause an imbalance in the sex ratio, including cultural preferences for males, gender-selective migration, and major military and ethnic conflicts. Unbalanced sex ratios can have serious social ramifications. Cultural Preferences for Males Some cultures demonstrate a marked preference for males, a phenomenon called androcentrism . India and China are two good examples, but androcentrism also exists in many other parts of the world. The cultural preference for males is rooted in history. In most societies, men have long held positions of economic, political, social, and cultural power and prestige. Men are typically considered to be the heads of households, and family names and, with them, family honor and wealth tend to pass from father to son. In India, male babies are strongly preferred. In China, newly married women traditionally would move to live in their in-laws%u2019 house. The sons were expected to assume economic responsibility for their aging parents. For all of these reasons, Chinese, Indian, and many other cultures place a premium on producing male children (see Subject to Debate: Female: An Endangered Gender?). Figure 8.6 shows geographical differences in The Sex Ratio 8-3 What is the sex ratio of a population? Another important aspect of population composition is the makeup of a population by sex. The sex ratio is the numerical ratio of males to females in the population. For example, India%u2019s sex ratio in 2019 was 107.48, meaning that there were 107.48 males for every 100 females in India. Usually more boys than girls are born, but infant boys have a slightly higher mortality rate than infant girls do, so the numbers of adult men and women tend to even out. However, the smaller the geographic unit, the more unbalanced the sex ratio probably will be. In addition, the sex ratio differs across age groups. Older cohorts often have more women than men because women often outlive men. TERMS TO KNOW sex ratio: The ratio of the number of men to number of women in a population androcentrism: A phenomenon in which a culture demonstrates a marked preference for males Tropic of CancerArctic CircleTropic of CapricornEquatorPACIFICOCEANPACIFICOCEANATLANTICOCEANATLANTICOCEANINDIANOCEAN20%u00b0N40%u00b0N60%u00b0N80%u00b0N20%u00b0N20%u00b0S40%u00b0S40%u00b0N60%u00b0N80%u00b0N0%u00b0120%u00b0W 100%u00b0W 80%u00b0W 60%u00b0W 40%u00b0W 20%u00b0W 0%u00b0 20%u00b0E 40%u00b0E 60%u00b0E 80%u00b0E 100%u00b0E 120%u00b0E 140%u00b0E 160%u00b0E 180%u00b0Tropic of CancerArctic CircleTropic of CapricornEquator0 2000 4000 miles0 2000 4000 km120%u00b0WPercent of the populationthat is female, 2022Above 5251.1%u20135250.1%u2013515049%u201349.948%u201348.9Below 48No dataFigure 8.6 Females as a percentage of total population. What spatial patterns of unbalanced sex ratios does this map%u00a0reveal? %u00a9 Bedford, Freeman & Worth Publishers. For review purposes only. Do not distribute.