Page 26 - 2024-bfw-MyersAP4e
P. 26
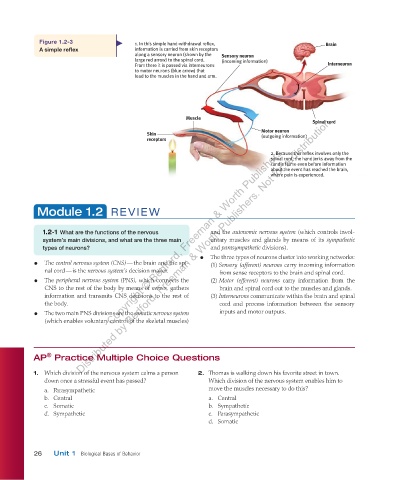
Figure 1.2-3 1. In this simple hand-withdrawal reflex, Brain
A simple reflex information is carried from skin receptors
along a sensory neuron (shown by the Sensory neuron
large red arrow) to the spinal cord. (incoming information)
From there it is passed via interneurons Interneuron
to motor neurons (blue arrow) that
lead to the muscles in the hand and arm.
Distributed by Bedford, Freeman & Worth Publishers. Not for redistribution.
Muscle
Spinal cord
Motor neuron
Skin (outgoing information)
receptors
Copyright © Bedford, Freeman & Worth Publishers.
2. Because this reflex involves only the
spinal cord, the hand jerks away from the
candle flame even before information
about the event has reached the brain,
where pain is experienced.
Module 1.2 REVIEW
1.2-1 What are the functions of the nervous and the autonomic nervous system (which controls invol-
system’s main divisions, and what are the three main untary muscles and glands by means of its sympathetic
types of neurons? and parasympathetic divisions).
• The three types of neurons cluster into working networks:
• The central nervous system (CNS) — the brain and the spi- (1) Sensory (afferent) neurons carry incoming information
nal cord — is the nervous system’s decision maker. from sense receptors to the brain and spinal cord.
• The peripheral nervous system (PNS), which connects the (2) Motor (efferent) neurons carry information from the
CNS to the rest of the body by means of nerves, gathers brain and spinal cord out to the muscles and glands.
information and transmits CNS decisions to the rest of (3) Interneurons communicate within the brain and spinal
the body. cord and process information between the sensory
• The two main PNS divisions are the somatic nervous system inputs and motor outputs.
(which enables voluntary control of the skeletal muscles)
®
AP Practice Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which division of the nervous system calms a person 2. Thomas is walking down his favorite street in town.
down once a stressful event has passed? Which division of the nervous system enables him to
a. Parasympathetic move the muscles necessary to do this?
b. Central a. Central
c. Somatic b. Sympathetic
d. Sympathetic c. Parasympathetic
d. Somatic
26 Unit 1 Biological Bases of Behavior
03_myersAPpsychology4e_28116_ch01_002_163.indd 26 15/12/23 9:21 AM