Page 23 - 2024-bfw-MyersAP4e
P. 23
Module 1.2
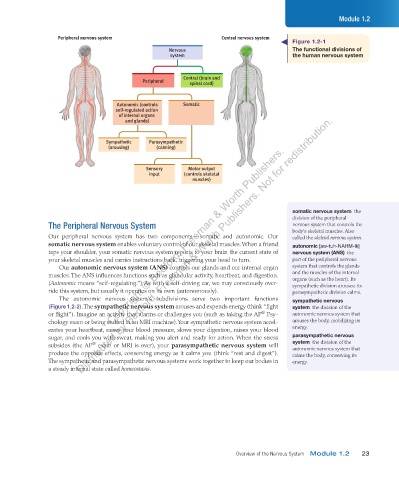
Peripheral nervous system Central nervous system
Figure 1.2-1
Nervous The functional divisions of
system the human nervous system
Central (brain and
Peripheral spinal cord)
Autonomic (controls Somatic
self-regulated action
of internal organs
Distributed by Bedford, Freeman & Worth Publishers. Not for redistribution.
and glands)
Sympathetic Parasympathetic
Copyright © Bedford, Freeman & Worth Publishers.
(arousing) (calming)
Sensory Motor output
input (controls skeletal
muscles)
somatic nervous system the
division of the peripheral
The Peripheral Nervous System nervous system that controls the
body’s skeletal muscles. Also
Our peripheral nervous system has two components — somatic and autonomic. Our called the skeletal nervous system.
somatic nervous system enables voluntary control of our skeletal muscles. When a friend autonomic [aw-tuh-NAHM-ik]
taps your shoulder, your somatic nervous system reports to your brain the current state of nervous system (ANS) the
your skeletal muscles and carries instructions back, triggering your head to turn. part of the peripheral nervous
Our autonomic nervous system (ANS) controls our glands and our internal organ system that controls the glands
muscles. The ANS influences functions such as glandular activity, heartbeat, and digestion. and the muscles of the internal
(Autonomic means “self-regulating.”) As with a self-driving car, we may consciously over- organs (such as the heart). Its
sympathetic division arouses; its
ride this system, but usually it operates on its own (autonomously). parasympathetic division calms.
The autonomic nervous system’s subdivisions serve two important functions sympathetic nervous
(Figure 1.2-2). The sympathetic nervous system arouses and expends energy (think “fight system the division of the
®
or flight”). Imagine an activity that alarms or challenges you (such as taking the AP Psy- autonomic nervous system that
chology exam or being stuffed in an MRI machine). Your sympathetic nervous system accel- arouses the body, mobilizing its
erates your heartbeat, raises your blood pressure, slows your digestion, raises your blood energy.
sugar, and cools you with sweat, making you alert and ready for action. When the stress parasympathetic nervous
®
subsides (the AP exam or MRI is over), your parasympathetic nervous system will system the division of the
autonomic nervous system that
produce the opposite effects, conserving energy as it calms you (think “rest and digest”). calms the body, conserving its
The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems work together to keep our bodies in energy.
a steady internal state called homeostasis.
Overview of the Nervous System Module 1.2 23
03_myersAPpsychology4e_28116_ch01_002_163.indd 23 15/12/23 9:21 AM