Page 28 - 2024-bfw-MyersAP4e
P. 28
Module 1.3a The Neuron and Neural Firing:
Neural Communication and
the Endocrine System
LEARNING TARGETS
Distributed by Bedford, Freeman & Worth Publishers. Not for redistribution.
1.3-1 Describe neurons, and explain how they transmit information.
1.3-2 Explain how nerve cells communicate with other nerve cells.
cell body the part of a neuron Copyright © Bedford, Freeman & Worth Publishers.
1.3-3 Explain how neurotransmitters influence behavior, and explain how drugs
and other chemicals affect neurotransmission.
1.3-4 Explain how the endocrine system transmits information and interacts with
the nervous system.
Neural Communication
For scientists, it is a happy fact of nature that the information systems of humans and other
animals operate similarly. This similarity allows researchers to study relatively simple animals
to discover how our own neural systems operate. Cars differ, but all have engines, accelera-
tors, steering wheels, and brakes. A space alien could study any one of them and grasp the
operating principles. Likewise, animals differ, yet their nervous systems operate similarly.
Neurons
What ar
e
e
e
neurons,
and how do they transmit information?
neurons,
What ar
What ar
1.3-1
1.3-1 What are neurons, and how do they transmit information?
Our body’s neural information system comprises a complexity built from simplicity. Its build-
ing blocks are neurons or nerve cells. Throughout life, new neurons are born and unused
,
neuron a nerve cell; the basic neurons wither away ( O’Leary et al., 2014 ; Shors, 2014 ). To fathom our thoughts and actions,
building block of the nervous our memories and moods, we must first understand how neurons work and communicate.
system.
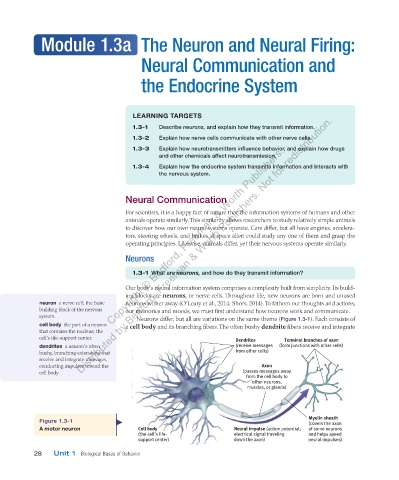
Neurons differ, but all are variations on the same theme ( Figure 1.3-1 ). Each consists of
a cell body and its branching fibers. The often bushy dendrite fibers receive and integrate
that contains the nucleus; the
cell’s life-support center. Dendrites Terminal branches of axon
dendrites a neuron’s often (receive messages (form junctions with other cells)
bushy, branching extensions that from other cells)
receive and integrate messages,
conducting impulses toward the Axon
cell body. (passes messages away
from the cell body to
other neurons,
muscles, or glands)
Figure 1.3-1 Myelin sheath
(covers the axon
A motor neuron Cell body Neural impulse (action potential; of some neurons
(the cell’s life- electrical signal traveling and helps speed
support center) down the axon) neural impulses)
28 Unit 1 Biological Bases of Behavior
03_myersAPpsychology4e_28116_ch01_002_163.indd 28 15/12/23 9:21 AM