Page 4 - Demo
P. 4
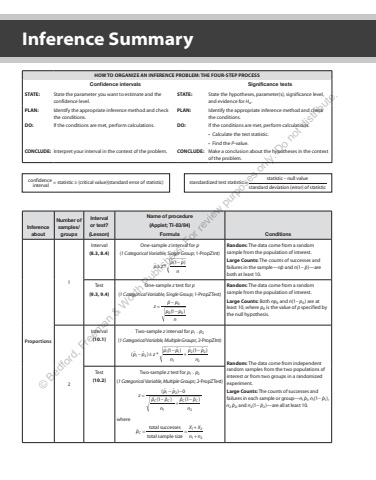
2 TablesInference SummaryHOW TO ORGANIZE AN INFERENCE PROBLEM: THE FOUR-STEP PROCESSConfidence intervals Significance testsSTATE: State the parameter you want to estimate and the confidence level.STATE: State the hypotheses, parameter(s), significance level, and evidence for Ha .PLAN: Identify the appropriate inference method and check the conditions.PLAN: Identify the appropriate inference method and check the conditions.DO: If the conditions are met, perform calculations. DO: If the conditions are met, perform calculations.%u2022 Calculate the test statistic.%u2022 Find the P-value.CONCLUDE: Interpret your interval in the context of the problem. CONCLUDE: Make a conclusion about the hypotheses in the context of the problem.Inference aboutNumber of samples/groupsInterval or test?(Lesson)Name of procedure(Applet; TI-83/84)Formula ConditionsProportions1Interval(8.3, 8.4)One-sample z interval for p(1 Categorical Variable, Single Group; 1-PropZInt)%u02c6 * %u02c6(1 %u02c6)%u00b1 %u2212 p zp pnRandom: The data come from a random sample from the population of interest.Large Counts: The counts of successes and failures in the sample%u2014np%u02c6 and n p (1%u2212 %u02c6)%u2014are both at least 10.Test(9.3, 9.4)One-sample z test for p(1 Categorical Variable, Single Group; 1-PropZTest)%u02c6(1 )00 0= %u2212%u2212 z p pp pnRandom: The data come from a random sample from the population of interest.Large Counts: Both np0 and (1 ) n p %u2212 0 are at least 10, where p0 is the value of p specified by the null hypothesis.2Interval(10.1)Two-sample z interval for 1 2 p p%u2212(1 Categorical Variable, Multiple Groups; 2-PropZInt)%u2212 %u00b1 %u2212 + %u2212 ( %u02c6 %u02c6 ) * %u02c6 (1 %u02c6 ) %u02c6 (1 %u02c6 ) 1 21 112 22p p z p pnp pn Random: The data come from independent random samples from the two populations of interest or from two groups in a randomized experiment.Large Counts: The counts of successes and failures in each sample or group%u2014 %u02c6 n p1 1, (1 %u02c6 ) n p 1 1 %u2212 , %u02c6 n p2 2, and (1 %u02c6 ) n p 2 2 %u2212 %u2014are all at least 10.Test(10.2)Two-sample z test for 1 2 p p%u2212(1 Categorical Variable, Multiple Groups; 2-PropZTest)( %u02c6 %u02c6 ) 0%u02c6 (1 %u02c6 ) %u02c6 (1 %u02c6 )1 21 2= %u2212 %u2212%u2212 + %u2212 z p pp pnp pnC C C Cwhere = = ++%u02c6 total successestotal sample size1 21 2pX Xn n Cconfidenceinterval = statistic ( %u00b1 critical value)(standard error of statistic) standardized test statistic = statistic null valuestandard deviation (error) of statistic%u2212%u00a9 Bedford, Freeman & Worth Publishers. For review purposes only. Do not distribute.