Page 29 - Demo
P. 29
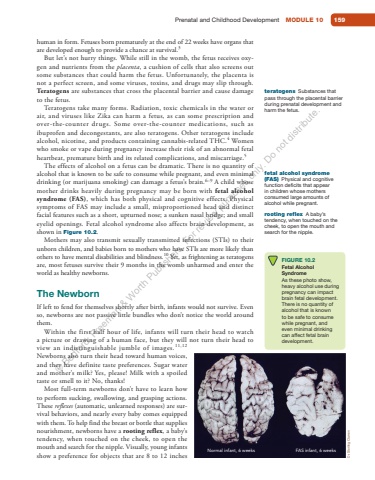
Prenatal and Childhood Development MODULE 10 159human in form. Fetuses born prematurely at the end of 22 weeks have organs that are developed enough to provide a chance at survival. 3 But let%u2019s not hurry things. While still in the womb, the fetus receives oxygen and nutrients from the placenta , a cushion of cells that also screens out some substances that could harm the fetus. Unfortunately, the placenta is not a perfect screen, and some viruses, toxins, and drugs may slip through. Teratogens are substances that cross the placental barrier and cause damage to the fetus. Teratogens take many forms. Radiation, toxic chemicals in the water or air, and viruses like Zika can harm a fetus, as can some prescription and over-the-counter drugs. Some over-the-counter medications, such as ibuprofen and decongestants, are also teratogens. Other teratogens include alcohol, nicotine, and products containing cannabis-related THC. 4 Women who smoke or vape during pregnancy increase their risk of an abnormal fetal heartbeat, premature birth and its related complications, and miscarriage. 5 The effects of alcohol on a fetus can be dramatic. There is no quantity of alcohol that is known to be safe to consume while pregnant, and even minimal drinking (or marijuana smoking) can damage a fetus%u2019s brain. 6 %u2013 9 A child whose mother drinks heavily during pregnancy may be born with fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS), which has both physical and cognitive effects. Physical symptoms of FAS may include a small, misproportioned head and distinct facial features such as a short, upturned nose; a sunken nasal bridge; and small eyelid openings. Fetal alcohol syndrome also affects brain development, as shown in Figure 10.2. Mothers may also transmit sexually transmitted infections (STIs) to their unborn children, and babies born to mothers who have STIs are more likely than others to have mental disabilities and blindness. 10 Yet, as frightening as teratogens are, most fetuses survive their 9 months in the womb unharmed and enter the world as healthy newborns. The Newborn If left to fend for themselves shortly after birth, infants would not survive. Even so, newborns are not passive little bundles who don%u2019t notice the world around them. Within the first half hour of life, infants will turn their head to watch a picture or drawing of a human face, but they will not turn their head to view an indistinguishable jumble of images. 11 , 12 Newborns also turn their head toward human voices, and they have definite taste preferences. Sugar water and mother%u2019s milk? Yes, please! Milk with a spoiled taste or smell to it? No, thanks! Most full-term newborns don%u2019t have to learn how to perform sucking, swallowing, and grasping actions. These reflexes (automatic, unlearned responses) are survival behaviors, and nearly every baby comes equipped with them. To help find the breast or bottle that supplies nourishment, newborns have a rooting reflex, a baby%u2019s tendency, when touched on the cheek, to open the mouth and search for the nipple. Visually, young infants show a preference for objects that are 8 to 12 inches teratogens Substances that pass through the placental barrier during prenatal development and harm the fetus. fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) Physical and cognitive function deficits that appear in children whose mothers consumed large amounts of alcohol while pregnant. FIGURE 10.2 Fetal Alcohol Syndrome As these photo show, heavy alcohol use during pregnancy can impact brain fetal development. There is no quantity of alcohol that is known to be safe to consume while pregnant, and even minimal drinking can affect fetal brain development. rooting reflex A baby%u2019s tendency, when touched on the cheek, to open the mouth and search for the nipple. Normal infant, 6 weeks FAS infant, 6 weeks Dr. Sterling Clarren%u00a9 Bedford, Freeman & Worth Publishers. For review purposes only. Do not distribute.