Page 33 - Demo
P. 33
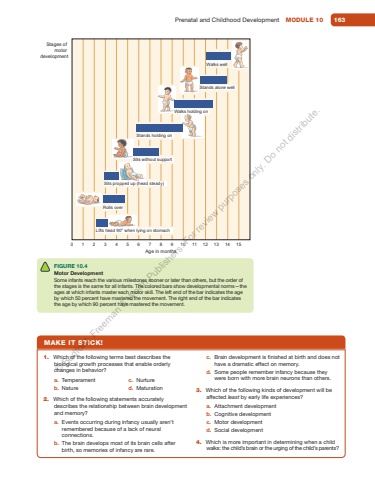
Prenatal and Childhood Development MODULE 10 1630Age in months123 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15Stages of motor developmentWalks wellStands alone wellWalks holding onStands holding onSits without supportSits propped up (head steady)Rolls overLifts head 90%u00b0 when lying on stomachFIGURE 10.4 Motor DevelopmentSome infants reach the various milestones sooner or later than others, but the order of the stages is the same for all infants. The colored bars show developmental norms%u2014the ages at which infants master each motor skill. The left end of the bar indicates the age by which 50 percent have mastered the movement. The right end of the bar indicates the age by which 90 percent have mastered the movement.MAKE IT STICK!1. Which of the following terms best describes the biological growth processes that enable orderly changes in behavior?a. Temperamentb. Naturec. Nurtured. Maturation2. Which of the following statements accurately describes the relationship between brain development and memory?a. Events occurring during infancy usually aren%u2019t remembered because of a lack of neural connections.b. The brain develops most of its brain cells after birth, so memories of infancy are rare.c. Brain development is finished at birth and does not have a dramatic effect on memory.d. Some people remember infancy because they were born with more brain neurons than others.3. Which of the following kinds of development will be affected least by early life experiences?a. Attachment developmentb. Cognitive developmentc. Motor developmentd. Social development4. Which is more important in determining when a child walks: the child%u2019s brain or the urging of the child%u2019s parents?%u00a9 Bedford, Freeman & Worth Publishers. For review purposes only. Do not distribute.