Page 69 - 2024-bfw-MyersAP4e
P. 69
Module 1.4b
The Hippocampus
The hippocampus is a curved brain structure that pro-
cesses conscious, explicit memories. Humans who lose
their hippocampus to surgery or injury also lose their
ability to form new memories of facts and events ( Clark
& Maguire, 2016 ). Those who survive a hippocampal brain
tumor in childhood struggle to remember new informa-
tion in adulthood ( Jayakar et al., 2015 ). National Football
League (NFL) players who experience one or more loss-of-
consciousness concussions may later have a shrunken
hippocampus and poor memory (Strain et al., 2015;
Tharmaratnam et al., 2018). Hippocampus size and function
decrease as we grow older, which furthers cognitive decline Elise Amendola/AP Images
( O’Callaghan et al., 2019 ; see Module 3.2). Modules 2.5 and
Copyright © Bedford, Freeman & Worth Publishers.
2.7 explain how our two-track mind uses the hippocampus
to process our memories. Are football players’ brains protected? When researchers analyzed the
brains of 111 deceased National Football League players, 99 percent showed
* * * signs of degeneration related to frequent head trauma ( Mez et al., 2017 . In 2017,
)
NFL player Aaron Hernandez (#81) died by suicide while imprisoned for murder.
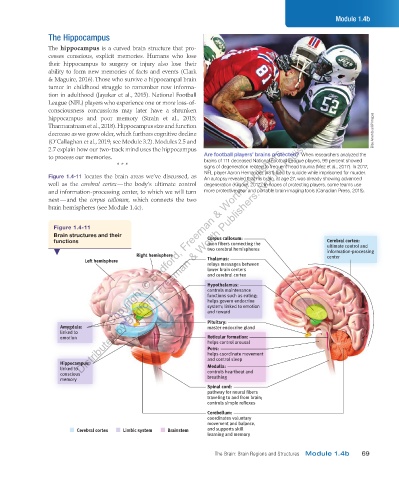
Figure 1.4-11 locates the brain areas we’ve discussed, as An autopsy revealed that his brain, at age 27, was already showing advanced
well as the cerebral cortex — the body’s ultimate control degeneration ( Kilgore, 2017 . In hopes of protecting players, some teams use
)
)
and information-processing center, to which we will turn more protective gear and portable brain-imaging tools ( Canadian Press, 2018 .
next — and the corpus callosum, which connects the two
brain hemispheres (see Module 1.4c).
Figure 1.4-11
Brain structures and their
Corpus callosum:
functions Distributed by Bedford, Freeman & Worth Publishers. Not for redistribution. Cerebral cortex:
axon fibers connecting the
two cerebral hemispheres ultimate control and
information-processing
Right hemisphere center
Left hemisphere Thalamus:
relays messages between
lower brain centers
and cerebral cortex
Hypothalamus:
controls maintenance
functions such as eating;
helps govern endocrine
system; linked to emotion
and reward
Pituitary:
Amygdala: master endocrine gland
linked to
emotion Reticular formation:
helps control arousal
Pons:
helps coordinate movement
and control sleep
Hippocampus:
linked to Medulla:
conscious controls heartbeat and
memory breathing
Spinal cord:
pathway for neural fibers
traveling to and from brain;
controls simple reflexes
Cerebellum:
coordinates voluntary
movement and balance,
Cerebral cortex Limbic system Brainstem and supports skill
learning and memory
The Brain: Brain Regions and Structures Module 1.4b 69
03_myersAPpsychology4e_28116_ch01_002_163.indd 69 15/12/23 9:23 AM