Page 64 - 2024-bfw-MyersAP4e
P. 64
®
AP Exam Tip the forebrain; it also controls some movement and transmits information that enables
our seeing and hearing. The forebrain manages complex cognitive activities, sen-
Your authors are about to take you sory and associative functions, and voluntary motor activities ( F igure 1.4-6 ) . Individual
on a journey through your brain. organisms’ brains have evolved to best suit their environment ( Cesario et al., 2020 ).
Focus on the name of each part, We humans, for example, have extremely well-developed forebrains, allowing us an
its location within the brain, and unparalleled ability to make complex decisions and judgments. Predatory sharks have
what it does. Then it’s time to
practice, practice, practice. The complex hindbrains, supporting their impressive ability to chase down prey ( Yopak
brain structures have been on et al., 2010 ).
®
previous AP exams.
Distributed by Bedford, Freeman & Worth Publishers. Not for redistribution.
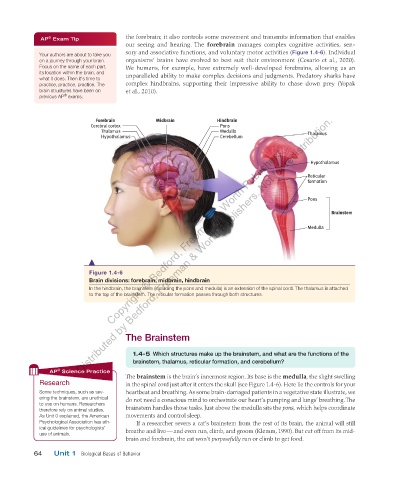
Forebrain Midbrain Hindbrain
Cerebral cortex Pons
Thalamus Medulla Thalamus
Hypothalamus Cerebellum
Copyright © Bedford, Freeman & Worth Publishers.
Hypothalamus
Reticular
formation
Pons
Brainstem
Medulla
Figure 1.4-6
Brain divisions: forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain
In the hindbrain, the brainstem (including the pons and medulla) is an extension of the spinal cord. The thalamus is attached
to the top of the brainstem. The reticular formation passes through both structures.
The Brainstem
Which structur
e the functions of the
es make up the brainstem, and what ar
1.4-5
1.4-5 Which structures make up the brainstem, and what are the functions of the
brainstem, thalamus, reticular formation, and cerebellum?
brainstem, thalamus, reticular formation, and cerebellum?
®
AP Science Practice
,
The brainstem is the brain’s innermost region. Its base is the medulla the slight swelling
Research in the spinal cord just after it enters the skull (see Figure 1.4-6 ). Here lie the controls for your
Some techniques, such as sev- heartbeat and breathing. As some brain-damaged patients in a vegetative state illustrate, we
ering the brainstem, are unethical do not need a conscious mind to orchestrate our heart’s pumping and lungs’ breathing. The
to use on humans. Researchers
therefore rely on animal studies. brainstem handles those tasks. Just above the medulla sits the pons, which helps coordinate
As Unit 0 explained, the American movements and control sleep.
Psychological Association has eth- If a researcher severs a cat’s brainstem from the rest of its brain, the animal will still
ical guidelines for psychologists’ breathe and live — and even run, climb, and groom ( Klemm, 1990 ). But cut off from its mid-
use of animals.
brain and forebrain, the cat won’t purposefully run or climb to get food.
64 Unit 1 Biological Bases of Behavior
03_myersAPpsychology4e_28116_ch01_002_163.indd 64 15/12/23 9:22 AM