Page 61 - 2022-bfw-morris-1e
P. 61
pyrimidines, the backbones would narrow. In both cases, A and T are held
there would be excessive strain on the covalent bonds in the together by two
hydrogen bonds.
sugar–phosphate backbone. The pairing of one purine (with
©2022 BFW Publishers. PAGES NOT FINAL. For review purposes only - do not post.
one ring) and one pyrimidine (with two rings) preserves N H
the distance between the backbones along the length of the N H O CH 3
entire molecule. N N H N
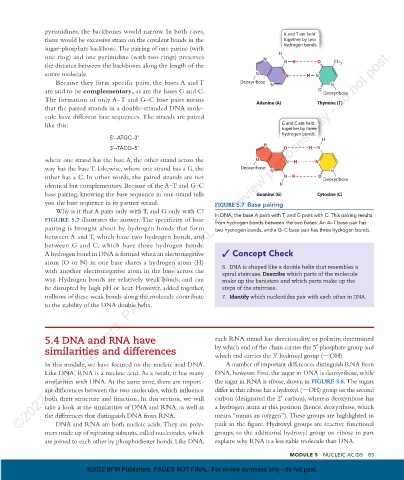
Because they form specific pairs, the bases A and T Deoxyribose N N N
are said to be complementary , as are the bases G and C. O Deoxyribose
The formation of only A–T and G–C base pairs means Adenine (A) Thymine (T)
that the paired strands in a double-stranded DNA mole-
cule have different base sequences. The strands are paired
like this: G and C are held
together by three
hydrogen bonds.
5’–ATGC–3’ H
N
3’–TACG–5’ O H N N N
where one strand has the base A, the other strand across the N N H N
way has the base T. Likewise, where one strand has a G, the Deoxyribose N N N
other has a C. In other words, the paired strands are not N H O Deoxyribose
identical but complementary. Because of the A–T and G–C H
base pairing, knowing the base sequence in one strand tells Guanine (G) Cytosine (C)
you the base sequence in its partner strand. FIGURE 5.7 Base pairing
Why is it that A pairs only with T, and G only with C?
FIGURE 5.7 illustrates the answer. The specificity of base In DNA, the base A pairs with T, and G pairs with C. This pairing results
from hydrogen bonds between the two bases. An A–T base pair has
pairing is brought about by hydrogen bonds that form two hydrogen bonds, and a G–C base pair has three hydrogen bonds.
between A and T, which have two hydrogen bonds, and
between G and C, which have three hydrogen bonds.
A hydrogen bond in DNA is formed when an electro negative Concept Check
atom (O or N) in one base shares a hydrogen atom (H)
6. DNA is shaped like a double helix that resembles a
with another electronegative atom in the base across the spiral staircase. Describe which parts of the molecule
way. Hydrogen bonds are relatively weak bonds, and can make up the banisters and which parts make up the
be disrupted by high pH or heat. However, added together, steps of the staircase.
millions of these weak bonds along the molecule contribute 7. Identify which nucleotides pair with each other in DNA.
to the stability of the DNA double helix.
5.4 DNA and RNA have each RNA strand has directionality, or polarity, determined
similarities and differences by which end of the chain carries the 5′ phosphate group and
which end carries the 3′ hydroxyl group (OOH).
In this module, we have focused on the nucleic acid DNA. A number of important differences distinguish RNA from
Like DNA, RNA is a nucleic acid. As a result, it has many DNA, however. First, the sugar in DNA is deoxyribose, while
similarities with DNA. At the same time, there are import- the sugar in RNA is ribose, shown in FIGURE 5.8 . The sugars
ant differences between the two molecules, which influence differ in that ribose has a hydroxyl (OOH) group on the second
both their structure and function. In this section, we will carbon (designated the 2′ carbon), whereas deoxyribose has
take a look at the similarities of DNA and RNA, as well as a hydrogen atom at this position (hence, deoxy ribose, which
the differences that distinguish DNA from RNA. means “minus an oxygen”). These groups are highlighted in
DNA and RNA are both nucleic acids. They are poly- pink in the figure. Hydroxyl groups are reactive functional
mers made up of repeating subunits, called nucleotides, which groups, so the additional hydroxyl group on ribose in part
are joined to each other by phosphodiester bonds. Like DNA, explains why RNA is a less stable molecule than DNA.
MODULE 5 Nucleic Acids 83
©2022 BFW Publishers. PAGES NOT FINAL. For review purposes only - do not post.
08_morrisapbiology1e_11331_Unit1_Mod5_78-91_2pp.indd 83 30/03/21 9:54 AM