Page 57 - 2022-bfw-morris-1e
P. 57
NH 2 O on. In deoxyribose, the 2′ carbon has a H atom, and the
N N 3′ carbon has a hydroxyl group.
N NH
The third component of a nucleotide is a phosphate
©2022 BFW Publishers. PAGES NOT FINAL. For review purposes only - do not post.
N N N N NH 2 group, shown in Figure 5.1. A phosphate group consists of
Adenine (A) Guanine (G) a central phosphorus (P) atom covalently bound to four
Purines oxygen atoms. Recall from Module 3 that a phosphate
O NH 2 group is a functional group with the properties of being
CH 3 polar and negatively charged. Note in Figure 5.1 that the
N N
phosphate group is attached to the 5′ carbon and it has neg-
N O N O ative charges on two of its oxygen atoms. These charges are
present because at cellular pH (around 7), the free hydroxyl
Thymine (T) Cytosine (C) groups attached to the phosphorus atom are ionized by the
Pyrimidines
loss of a proton and, therefore, are negatively charged. These
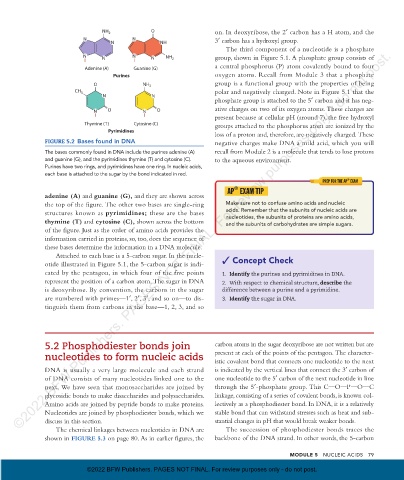
FIGURE 5.2 Bases found in DNA negative charges make DNA a mild acid, which you will
The bases commonly found in DNA include the purines adenine (A) recall from Module 2 is a molecule that tends to lose protons
and guanine (G), and the pyrimidines thymine (T) and cytosine (C). to the aqueous environment.
Purines have two rings, and pyrimidines have one ring. In nucleic acids,
each base is attached to the sugar by the bond indicated in red.
®
PREP FOR THE AP EXAM
®
AP EXAM TIP
adenine (A) and guanine (G) , and they are shown across
the top of the figure. The other two bases are single-ring Make sure not to confuse amino acids and nucleic
structures known as pyrimidines; these are the bases acids. Remember that the subunits of nucleic acids are
nucleotides, the subunits of proteins are amino acids,
thymine (T) and cytosine (C) , shown across the bottom and the subunits of carbohydrates are simple sugars.
of the figure. Just as the order of amino acids provides the
information carried in proteins, so, too, does the sequence of
these bases determine the information in a DNA molecule.
Attached to each base is a 5-carbon sugar. In the nucle-
otide illustrated in Figure 5.1, the 5-carbon sugar is indi- Concept Check
cated by the pentagon, in which four of the five points 1. Identify the purines and pyrimidines in DNA.
represent the position of a carbon atom. The sugar in DNA 2. With respect to chemical structure, describe the
is deoxyribose. By convention, the carbons in the sugar difference between a purine and a pyrimidine.
are numbered with primes—1′, 2′, 3′, and so on—to dis- 3. Identify the sugar in DNA.
tinguish them from carbons in the base—1, 2, 3, and so
5.2 Phosphodiester bonds join carbon atoms in the sugar deoxyribose are not written but are
nucleotides to form nucleic acids present at each of the points of the pentagon. The character-
istic covalent bond that connects one nucleotide to the next
DNA is usually a very large molecule and each strand is indicated by the vertical lines that connect the 3′ carbon of
of DNA consists of many nucleotides linked one to the one nucleotide to the 5′ carbon of the next nucleotide in line
next. We have seen that monosaccharides are joined by through the 5′-phosphate group. This OO OOCO P O C
glycosidic bonds to make disaccharides and polysaccharides. linkage, consisting of a series of covalent bonds, is known col-
Amino acids are joined by peptide bonds to make proteins. lectively as a phosphodiester bond. In DNA, it is a relatively
Nucleotides are joined by phosphodiester bonds, which we stable bond that can withstand stresses such as heat and sub-
discuss in this section. stantial changes in pH that would break weaker bonds.
The chemical linkages between nucleotides in DNA are The succession of phosphodiester bonds traces the
shown in FIGURE 5.3 on page 80. As in earlier figures, the backbone of the DNA strand. In other words, the 5-carbon
MODULE 5 Nucleic Acids 79
©2022 BFW Publishers. PAGES NOT FINAL. For review purposes only - do not post.
08_morrisapbiology1e_11331_Unit1_Mod5_78-91_2pp.indd 79 30/03/21 9:54 AM