Page 62 - 2022-bfw-morris-1e
P. 62
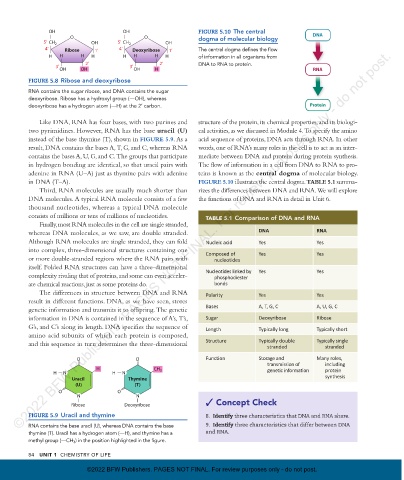
OH OH FIGURE 5.10 The central
O O dogma of molecular biology DNA
5’ CH 2 OH 5’ CH 2 OH
4’ Ribose 1’ 4’ Deoxyribose 1’ The central dogma defines the flow
©2022 BFW Publishers. PAGES NOT FINAL. For review purposes only - do not post.
H H H H H H H H of information in all organisms from
2’ 2’ DNA to RNA to protein.
3’ 3’
OH OH OH H RNA
FIGURE 5.8 Ribose and deoxyribose
RNA contains the sugar ribose, and DNA contains the sugar
deoxyribose. Ribose has a hydroxyl group (OOH), whereas
deoxyribose has a hydrogen atom (OH) at the 2′ carbon. Protein
Like DNA, RNA has four bases, with two purines and structure of the protein, its chemical properties, and its biologi-
two pyrimidines. However, RNA has the base uracil (U) cal activities, as we discussed in Module 4. To specify the amino
instead of the base thymine (T), shown in FIGURE 5.9 . As a acid sequence of proteins, DNA acts through RNA. In other
result, DNA contains the bases A, T, G, and C, whereas RNA words, one of RNA’s many roles in the cell is to act as an inter-
contains the bases A, U, G, and C. The groups that participate mediate between DNA and protein during protein synthesis.
in hydrogen bonding are identical, so that uracil pairs with The flow of information in a cell from DNA to RNA to pro-
adenine in RNA (U–A) just as thymine pairs with adenine teins is known as the central dogma of molecular biology.
in DNA (T–A). FIGURE 5.10 illustrates the central dogma. TABLE 5.1 summa-
Third, RNA molecules are usually much shorter than rizes the differences between DNA and RNA. We will explore
DNA molecules. A typical RNA molecule consists of a few the functions of DNA and RNA in detail in Unit 6.
thousand nucleotides, whereas a typical DNA molecule
consists of millions or tens of millions of nucleotides. TABLE 5.1 Comparison of DNA and RNA
Finally, most RNA molecules in the cell are single stranded,
whereas DNA molecules, as we saw, are double stranded. DNA RNA
Although RNA molecules are single stranded, they can fold Nucleic acid Yes Yes
into complex, three-dimensional structures containing one Composed of Yes Yes
or more double-stranded regions where the RNA pairs with nucleotides
itself. Folded RNA structures can have a three- dimensional Nucleotides linked by Yes Yes
complexity rivaling that of proteins, and some can even acceler- phosphodiester
ate chemical reactions, just as some proteins do. bonds
The differences in structure between DNA and RNA Polarity Yes Yes
result in different functions. DNA, as we have seen, stores
genetic information and transmits it to offspring. The genetic Bases A, T, G, C A, U, G, C
information in DNA is contained in the sequence of A’s, T’s, Sugar Deoxyribose Ribose
G’s, and C’s along its length. DNA specifies the sequence of Length Typically long Typically short
amino acid subunits of which each protein is composed,
and this sequence in turn determines the three-dimensional Structure Typically double Typically single
stranded
stranded
O O Function Storage and Many roles,
transmission of including
H CH 3 genetic information protein
H N H N synthesis
Uracil Thymine
(U) (T)
O O
N N
Ribose Deoxyribose Concept Check
FIGURE 5.9 Uracil and thymine 8. Identify three characteristics that DNA and RNA share.
RNA contains the base uracil (U), whereas DNA contains the base 9. Identify three characteristics that differ between DNA
thymine (T). Uracil has a hydrogen atom (OH), and thymine has a and RNA.
methyl group (OCH 3 ) in the position highlighted in the figure.
84 UNIT 1 cHeMisTRY OF liFe
©2022 BFW Publishers. PAGES NOT FINAL. For review purposes only - do not post.
08_morrisapbiology1e_11331_Unit1_Mod5_78-91_2pp.indd 84 30/03/21 9:54 AM