Page 127 - 2024-bfw-MyersAP4e
P. 127
Module 1.6b
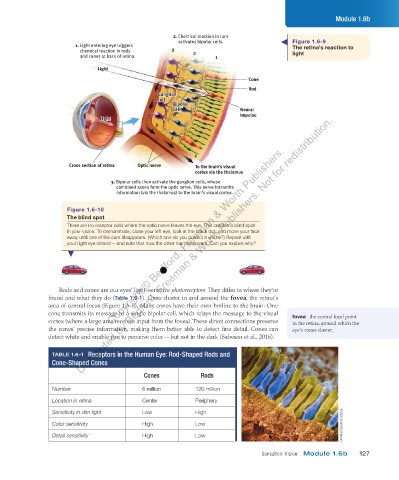
2. Chemical reaction in turn
activates bipolar cells. Figure 1.6-9
1. Light entering eye triggers The retina’s reaction to
chemical reaction in rods 3 2 light
and cones at back of retina. 1
Light
Cone
Rod
Ganglion
Ganglion
cell
cell
Bipolar
Bipolar
cell
cell Neural
impulse
Distributed by Bedford, Freeman & Worth Publishers. Not for redistribution.
Light
Light
3
2
Copyright © Bedford, Freeman & Worth Publishers.
1
Cross section of retina Optic nerve To the brain’s visual
cortex via the thalamus
3. Bipolar cells then activate the ganglion cells, whose
combined axons form the optic nerve. This nerve transmits
information (via the thalamus) to the brain’s visual cortex.
Figure 1.6-10
The blind spot
There are no receptor cells where the optic nerve leaves the eye. This creates a blind spot
in your vision. To demonstrate, close your left eye, look at the black dot, and move your face
away until one of the cars disappears. (Which one do you predict it will be?) Repeat with
your right eye closed — and note that now the other car disappears. Can you explain why?
Rods and cones are our eyes’ light-sensitive photoreceptors. They differ in where they’re
found and what they do (Table 1.6-1). Cones cluster in and around the fovea, the retina’s
area of central focus (Figure 1.6-8). Many cones have their own hotline to the brain: One
cone transmits its message to a single bipolar cell, which relays the message to the visual fovea the central focal point
cortex (where a large area receives input from the fovea). These direct connections preserve in the retina, around which the
the cones’ precise information, making them better able to detect fine detail. Cones can eye’s cones cluster.
detect white and enable you to perceive color — but not in the dark (Sabesan et al., 2016).
TABLE 1.6-1 Receptors in the Human Eye: Rod-Shaped Rods and
Cone-Shaped Cones
Cones Rods
Number 6 million 120 million
Location in retina Center Periphery
Omikron/Science Source
Sensitivity in dim light Low High
Color sensitivity High Low
Detail sensitivity High Low
Sensation: Vision Module 1.6b 127
03_myersAPpsychology4e_28116_ch01_002_163.indd 127 15/12/23 9:25 AM