Page 61 - 2024-bfw-MyersAP4e
P. 61
Module 1.4a
One neuroscience team scanned 129 people’s brains as they did eight different mental
tasks (such as reading, gambling, or rhyming). Later, they were able, with 80 percent accu-
racy, to identify which of these mental activities the study participants had been doing
(Poldrack et al., 2018).
You’ve undoubtedly seen pictures of colorful “lit-up” brain regions with accompanying
headlines, such as “your brain on music.” Although brain areas don’t actually light up, vivid
brain scan images seem impressive. In fact, people have rated scientific explanations as more
believable and interesting when they contain neuroscience (Fernandez-Duque et al., 2015;
Im et al., 2017). But “neuroskeptics” caution against overblown claims about any ability to
predict customer preferences, to detect lies, and to foretell crime based on neuroscience
(Schwartz et al., 2016). Neuromarketing, neuroleadership, neurolaw, and neuropolitics are
i. fMRI scan Distributed by Bedford, Freeman & Worth Publishers. Not for redistribution.
often neurohype. Imaging techniques illuminate brain structure and activity, and sometimes
they can help us test different theories of behavior (Mather et al., 2013). But given that all
human experience is brain based, it’s no surprise that different brain areas become active
Copyright © Bedford, Freeman & Worth Publishers.
when one listens to a lecture or lusts for a lover.
Today’s techniques for peering into the thinking, feeling brain are doing for
psychology what the microscope did for biology and the telescope did for astronomy.
European researchers have undertaken a $1 billion Human Brain Project (Salles et al.,
2019). Another project is exploring brain aging from age 3 to 96 (Pomponio et al., 2020).
These massive undertakings harness
the collective power of hundreds of
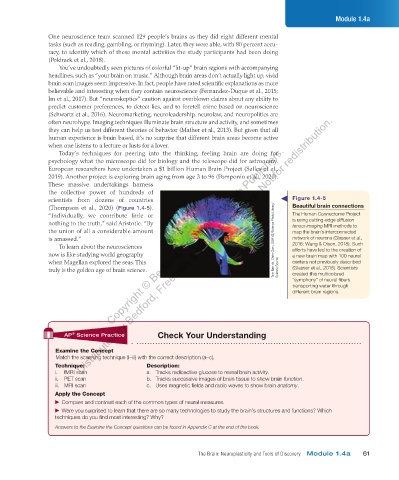
scientists from dozens of countries Figure 1.4-5
(Thompson et al., 2020) (Figure 1.4-5). Beautiful brain connections
“Individually, we contribute little or The Human Connectome Project
nothing to the truth,” said Aristotle. “By is using cutting-edge diffusion
tensor imaging MRI methods to
the union of all a considerable amount map the brain’s interconnected
is amassed.” Tom Barrick, Chris Clark, SGHMS/Science Photo Library/ network of neurons (Glasser et al.,
To learn about the neurosciences 2016; Wang & Olson, 2018). Such
efforts have led to the creation of
now is like studying world geography a new brain map with 100 neural
when Magellan explored the seas. This centers not previously described
truly is the golden age of brain science. Science Source (Glasser et al., 2016). Scientists
created this multicolored
“symphony” of neural fibers
transporting water through
different brain regions.
AP Science Practice Check Your Understanding
®
Examine the Concept
Match the scanning technique (i–iii) with the correct description (a–c).
Technique: Description:
a. Tracks radioactive glucose to reveal brain activity.
ii. PET scan b. Tracks successive images of brain tissue to show brain function.
iii. MRI scan c. Uses magnetic fields and radio waves to show brain anatomy.
Apply the Concept
▶ ▶Compare and contrast each of the common types of neural measures.
▶ ▶Were you surprised to learn that there are so many technologies to study the brain’s structures and functions? Which
techniques do you find most interesting? Why?
Answers to the Examine the Concept questions can be found in Appendix C at the end of the book.
The Brain: Neuroplasticity and Tools of Discovery Module 1.4a 61
03_myersAPpsychology4e_28116_ch01_002_163.indd 61 15/12/23 9:22 AM