Page 48 - bfw-APHG-1e
P. 48
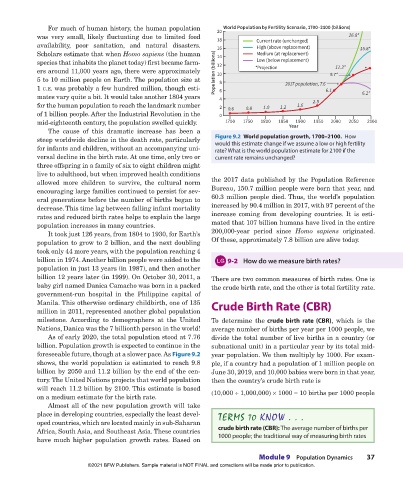
For much of human history, the human population 20 World Population by Fertility Scenario, 1700–2100 (billions)
was very small, likely fluctuating due to limited food 18 Current rate (unchanged) 26.8*
availability, poor sanitation, and natural disasters. 16 High (above replacement) 15.8*
Scholars estimate that when Homo sapiens (the human 14 Medium (at replacement)
species that inhabits the planet today) first became farm- 12 Low (below replacement)
ers around 11,000 years ago, there were approximately Population (billions) 10 *Projection 9.7* 11.2*
5 to 10 million people on Earth. The population size at 8 2017 population, 7.6
1 c.e. was probably a few hundred million, though esti- 6 6.1
mates vary quite a bit. It would take another 1804 years 4 6.2*
for the human population to reach the landmark number 2 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.6 2.5
of 1 billion people. After the Industrial Revolution in the 0
1900
mid-eighteenth century, the population swelled quickly. 1700 1750 1800 1850 Year 1950 2000 2050 2100
The cause of this dramatic increase has been a
steep worldwide decline in the death rate, particularly Figure 9.2 World population growth, 1700–2100. How
would this estimate change if we assume a low or high fertility
for infants and children, without an accompanying uni- rate? What is the world population estimate for 2100 if the
versal decline in the birth rate. At one time, only two or current rate remains unchanged?
three offspring in a family of six to eight children might
live to adulthood, but when improved health conditions
allowed more children to survive, the cultural norm the 2017 data published by the Population Reference
encouraging large families continued to persist for sev- Bureau, 150.7 million people were born that year, and
eral generations before the number of births began to 60.3 million people died. Thus, the world’s population
decrease. This time lag between falling infant mortality increased by 90.4 million in 2017, with 97 percent of the
rates and reduced birth rates helps to explain the large increase coming from developing countries. It is esti-
population increases in many countries. mated that 107 billion humans have lived in the entire
It took just 126 years, from 1804 to 1930, for Earth’s 200,000-year period since Homo sapiens originated.
population to grow to 2 billion, and the next doubling Of these, approximately 7.8 billion are alive today.
took only 44 more years, with the population reaching 4
billion in 1974. Another billion people were added to the 9-2 How do we measure birth rates?
population in just 13 years (in 1987), and then another
billion 12 years later (in 1999). On October 30, 2011, a There are two common measures of birth rates. One is
baby girl named Danica Camacho was born in a packed the crude birth rate, and the other is total fertility rate.
government-run hospital in the Philippine capital of
Manila. This otherwise ordinary childbirth, one of 135 Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
million in 2011, represented another global population
milestone. According to demographers at the United To determine the crude birth rate (CBR), which is the
Nations, Danica was the 7 billionth person in the world! average number of births per year per 1000 people, we
As of early 2020, the total population stood at 7.76 divide the total number of live births in a country (or
billion. Population growth is expected to continue in the subnational unit) in a particular year by its total mid-
foreseeable future, though at a slower pace. As Figure 9.2 year population. We then multiply by 1000. For exam-
shows, the world population is estimated to reach 9.8 ple, if a country had a population of 1 million people on
billion by 2050 and 11.2 billion by the end of the cen- June 30, 2019, and 10,000 babies were born in that year,
tury. The United Nations projects that world population then the country’s crude birth rate is
will reach 11.2 billion by 2100. This estimate is based (10,000 ÷ 1,000,000) × 1000 = 10 births per 1000 people
on a medium estimate for the birth rate.
Almost all of the new population growth will take
place in developing countries, especially the least devel- TERMS TO KNOW . . .
oped countries, which are located mainly in sub-Saharan
Africa, South Asia, and Southeast Asia. These countries crude birth rate (CBR): The average number of births per
1000 people; the traditional way of measuring birth rates
have much higher population growth rates. Based on
Module 9 Population Dynamics 37
©2021 BFW Publishers. Sample material is NOT FINAL and corrections will be made prior to publication.
02_Hildebrhgap1e_19224_unit02_002_131_4pp.indd 37 05/19/20 6:04 PM