Page 56 - bfw-APHG-1e
P. 56
AP® Exam Practice Questions Preparing for the AP® Exam
Multiple-Choice Questions 3. An increase in the aging population in a country
means that
1. Which of the following countries would have the
lowest rate of natural increase in population? a. its dependency ratio will be higher.
a. United States b. its economy will stagnate.
b. Nigeria c. there will be a greater need for playgrounds.
c. Australia d. it will have a minimal effect on the population.
d. Japan e. it will adversely affect the environment.
e. Ghana 4. Using the rule of 70, in how many years will the pop-
ulation of Mali double if its present rate of natural
2. Which of the following actions would have the greatest
effect in lowering the total fertility rate of a country? increase is 3.6, assuming all others indicators stay
a. Increase education for girls. constant?
b. Encourage out-migration. a. 20 years
c. Lower the age of marriage. b. 40 years
d. Deny women access to contraceptives. c. 60 years
e. Tax families with more than two children. d. 80 years
influences, education, gender roles, and population e. 100 years
policies.
Free Response Questions
EXAMPLE (parts a-g are worth 1 point each) EXAMPLE RUBRIC
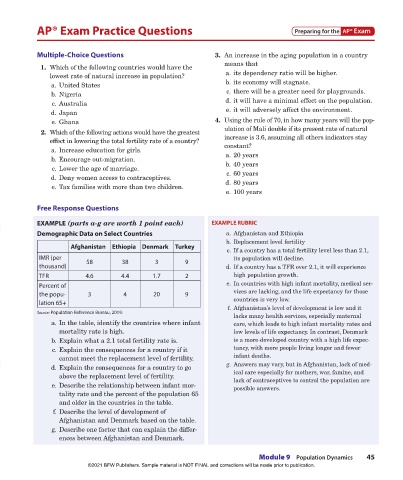
9-3 How do we measure death rates? Demographic Data on Select Countries a. Afghanistan and Ethiopia
• Crude death rate (CDR), or mortality rate, is the Afghanistan Ethiopia Denmark Turkey b. Replacement level fertility
number of deaths per year per 1000 people. The c. If a country has a total fertility level less than 2.1,
world’s CDR in 2018 was 7 deaths per 1000 people. IMR (per 58 38 3 9 its population will decline.
More-developed countries have slightly higher death thousand) d. If a country has a TFR over 2.1, it will experience
rates than less-developed countries because their TFR 4.6 4.4 1.7 2 high population growth.
populations are older. Percent of e. In countries with high infant mortality, medical ser-
• Infant mortality rate (IMR) measures how many the popu- 3 4 20 9 vices are lacking, and the life expectancy for those
countries is very low.
infants die in their first year per 1000 live births. lation 65+ f. Afghanistan’s level of development is low and it
It is considered the best single indicator of living Source: Population Reference Bureau, 2019. lacks many health services, especially maternal
standards. The world’s IMR is 31. Most developed a. In the table, identify the countries where infant care, which leads to high infant mortality rates and
countries have a low single-digit IMR, but develop- mortality rate is high. low levels of life expectancy. In contrast, Denmark
ing countries’ IMRs may be as high as 50–70. b. Explain what a 2.1 total fertility rate is. is a more-developed country with a high life expec-
c. Explain the consequences for a country if it tancy, with more people living longer and fewer
cannot meet the replacement level of fertility. infant deaths.
9-4 How do we measure natural increase? d. Explain the consequences for a country to go g. Answers may vary, but in Afghanistan, lack of med-
above the replacement level of fertility. ical care especially for mothers, war, famine, and
• Natural increase in population refers to the differ- lack of contraceptives to control the population are
ence between total births and deaths in a given year. e. Describe the relationship between infant mor- possible answers.
It is usually expressed as a percentage of total popu- tality rate and the percent of the population 65
lation, or the rate of natural increase (RNI). and older in the countries in the table.
• When birth rate equals death rate, a country reaches f. Describe the level of development of
zero population growth. There is no natural increase Afghanistan and Denmark based on the table.
in population (i.e., RNI = 0), but age and sex structure g. Describe one factor that can explain the differ-
may still change. ences between Afghanistan and Denmark.
Module 9 Population Dynamics 45
©2021 BFW Publishers. Sample material is NOT FINAL and corrections will be made prior to publication.
02_Hildebrhgap1e_19224_unit02_002_131_4pp.indd 45 05/19/20 6:04 PM