Page 54 - bfw-APHG-1e
P. 54
80°N 80°N
Arctic Circle
Arctic Circle
60°N 60°N
40°N 40°N
ATLANTIC
OCEAN Tropic of Cancer
Tropic of Cancer
20°N 20°N
PACIFIC PACIFIC
OCEAN OCEAN
Equator
0° Equator 0°
INDIAN
Annual population OCEAN
20°S increase, 2017 20°S
Tropic of Capricorn
Above 3% ATLANTIC Tropic of Capricorn
2.1–3% OCEAN
40°S 40°S
1–2% 0 2000 4000 miles
Below 1% 0 2000 4000 km
Decrease 120°W 100°W 80°W 60°W 40°W 20°W 0° 20°E 40°E 60°E 80°E 100°E 120°E 140°E 160°E 180°
160°W
160°W
140°W
120°W
100°W
140°W
No data
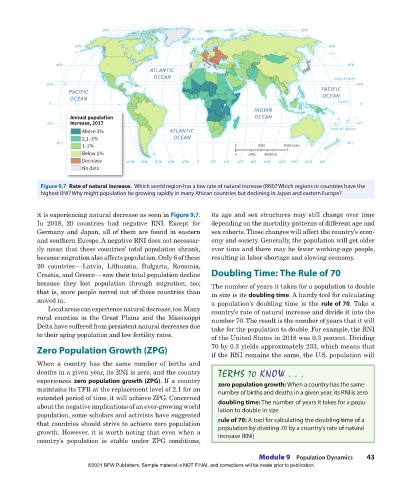
Figure 9.7 Rate of natural increase. Which world region has a low rate of natural increase (RNI)? Which regions or countries have the
highest RNI? Why might population be growing rapidly in many African countries but declining in Japan and eastern Europe?
it is experiencing natural decrease as seen in Figure 9.7. its age and sex structures may still change over time
In 2018, 20 countries had negative RNI. Except for depending on the mortality patterns of different age and
Germany and Japan, all of them are found in eastern sex cohorts. Those changes will affect the country’s econ-
and southern Europe. A negative RNI does not necessar- omy and society. Generally, the population will get older
ily mean that these countries’ total population shrank, over time and there may be fewer working-age people,
because migration also affects population. Only 6 of these resulting in labor shortage and slowing economy.
20 countries — Latvia, Lithuania, Bulgaria, Romania,
Croatia, and Greece — saw their total population decline Doubling Time: The Rule of 70
because they lost population through migration, too; The number of years it takes for a population to double
that is, more people moved out of these countries than in size is its doubling time. A handy tool for calculating
moved in. a population’s doubling time is the rule of 70. Take a
Local areas can experience natural decrease, too. Many country’s rate of natural increase and divide it into the
rural counties in the Great Plains and the Mississippi number 70. The result is the number of years that it will
Delta have suffered from persistent natural decreases due take for the population to double. For example, the RNI
to their aging population and low fertility rates. of the United States in 2018 was 0.3 percent. Dividing
Zero Population Growth (ZPG) 70 by 0.3 yields approximately 233, which means that
if the RNI remains the same, the U.S. population will
When a country has the same number of births and
deaths in a given year, its RNI is zero, and the country TERMS TO KNOW . . .
experiences zero population growth (ZPG). If a country zero population growth: When a country has the same
maintains its TFR at the replacement level of 2.1 for an number of births and deaths in a given year, its RNI is zero
extended period of time, it will achieve ZPG. Concerned doubling time: The number of years it takes for a popu-
about the negative implications of an ever-growing world lation to double in size
population, some scholars and activists have suggested
that countries should strive to achieve zero population rule of 70: A tool for calculating the doubling time of a
population by dividing 70 by a country’s rate of natural
growth. However, it is worth noting that even when a increase (RNI)
country’s population is stable under ZPG conditions,
Module 9 Population Dynamics 43
©2021 BFW Publishers. Sample material is NOT FINAL and corrections will be made prior to publication.
02_Hildebrhgap1e_19224_unit02_002_131_4pp.indd 43 05/19/20 6:04 PM