Page 30 - 2023-bfw-Macro-Krugman-Econ-4e
P. 30
ModULE 1.4
When economists talk about a “change in demand,” saying “the demand for X AP ECoN TIP
®
increased” or “the demand for Y decreased,” they mean that the demand curve for X or
Y shifted — not that the quantity demanded rose or fell because of a change in the price. When shifting curves, a
decrease is shown as a
Understanding Shifts of the demand Curve movement to the left, and
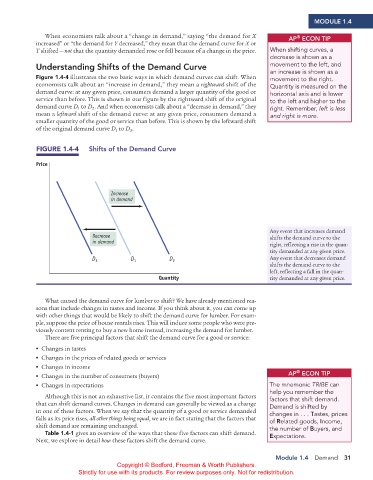
Figure 1.4-4 illustrates the two basic ways in which demand curves can shift. When an increase is shown as a
movement to the right.
economists talk about an “increase in demand,” they mean a rightward shift of the Quantity is measured on the
demand curve: at any given price, consumers demand a larger quantity of the good or horizontal axis and is lower
service than before. This is shown in our figure by the rightward shift of the original to the left and higher to the
demand curve D to D . And when economists talk about a “decrease in demand,” they right. Remember, left is less
2
1
mean a leftward shift of the demand curve: at any given price, consumers demand a and right is more.
smaller quantity of the good or service than before. This is shown by the leftward shift
of the original demand curve D to D .
3
1
FIGURE 1.4-4 Shifts of the demand Curve
Price
Increase
in demand
Any event that increases demand
Decrease shifts the demand curve to the
in demand right, reflecting a rise in the quan-
tity demanded at any given price.
D 3 D 1 D 2 Any event that decreases demand
shifts the demand curve to the
left, reflecting a fall in the quan-
Quantity tity demanded at any given price.
What caused the demand curve for lumber to shift? We have already mentioned rea-
sons that include changes in tastes and income. If you think about it, you can come up
with other things that would be likely to shift the demand curve for lumber. For exam-
ple, suppose the price of house rentals rises. This will induce some people who were pre-
viously content renting to buy a new home instead, increasing the demand for lumber.
There are five principal factors that shift the demand curve for a good or service:
• • Changes in tastes
• • Changes in the prices of related goods or services
• • Changes in income
®
• • Changes in the number of consumers (buyers) AP ECoN TIP
• • Changes in expectations The mnemonic TRIBE can
help you remember the
Although this is not an exhaustive list, it contains the five most important factors factors that shift demand.
that can shift demand curves. Changes in demand can generally be viewed as a change Demand is shifted by
in one of these factors. When we say that the quantity of a good or service demanded changes in . . . Tastes, prices
falls as its price rises, all other things being equal, we are in fact stating that the factors that of Related goods, Income,
shift demand are remaining unchanged. the number of Buyers, and
Table 1.4-1 gives an overview of the ways that these five factors can shift demand. Expectations.
Next, we explore in detail how these factors shift the demand curve.
Module 1.4 Demand 31
Copyright © Bedford, Freeman & Worth Publishers.
Strictly for use with its products. For review purposes only. Not for redistribution.
02_APKrugman4e_40932_MacroU01_002_062.indd 31 05/07/22 10:50 AM